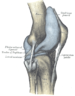
Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity.
Normal range of motion (ROM) of the knee joint is from 0 to 135 degrees in an adult. Full knee extension should be no more than 10 degrees. In genu recurvatum (back knee), normal extension is increased. The development of genu recurvatum, may lead to knee pain and knee osteoarthritis.
Hemiplegic patient have a common gait deviation during their gait training is hyper-extension of knee or genu recurvatum.
Cause of genu recurvatum are
1. Weakness of plantar flexors:
2. Flail foot i.e. polio, cerebral palsy etc
3. Tightness of plantar flexors (TA tendon)
Becouse of above factors patient shows a poor loading responce in gait.
In normals loading responce ankle goes from 10 degree of plantar flexon to 10 degree of relative dorsiflexion and knee in 10-20 degree of lexion. There is anterior translation of tibia over the fixed foot.
This anterior translation of tibia over the fied foot is affected due to TA tigthness.
In weakness of plantar flexors & flail foot if tibia moves over the fixed foot and goes in to relative dorsiflexion then this may lead to buckling of knee and lead to poor stability during loading responce to mid stance. to avoid this patient does the compansotory movement of, avoiding the anterior translation of tibia and forward lurching gait, with locking of knee. frequent use of this pattern of locking mechanism of knee during walk leads to hyperextension of knee.
1. in case of weakness of platar flexors , . flail foot & weakness in whole limb use HIGH AFO. That is the posterior strap of the AFO is hiogh enough up the lower margine of popliteal fossa.this long leverage prevents it from going backward.

2.But this will not work in patients who walk with forward lurch posture or those who take bigger step length of opposite unaffected leg.the solution for this is very simple reduce the step length of opposite leg and allow him to step by the affected leg instead of going ahead. this will pull back the line of gravity which was falling forward to knee and reduce hyper extension.
3. In the patients having sever hyeperextension and can't be corrected by all these measures then the last solution is use KAFO for walking.
4. knee surgery are not successful for preventing hyperextesnion.
5. In TA tightness -do stretching but the effect doesn't last longer in the functional activity of walking. so we should give functional stretching. for this use modified AFO{FRO} : shift the calf bad of AFO anteriorly this produces good three point pressure phenomenon and helps in stretching the TA in functional activity of walking and helps in reducing recurvatum.
6. In cases Poor trunk control and imbalance or low postural tone ( Down & hypotonic CP. wok on postural tone , trunk control in addition give AFO & walker with forearm support this reduces the forward flexion of trunk.
References
1. WHO | Stroke, Cerebrovascular accident [Internet]. [cited 2010 Aug 3]; Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/cerebrovascular accident/en
2. Tapas kumar banerjee et al. Epidemiology of stroke in India. Journal of Neurology Asia.2006;11:1-4.
3. Edward R. Laskowski, M.D. Hyperextended knee: Cause of serious injury http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hyperextended-knee/AN00283
4. Jennifer Kirkman, Yahoo! Contributor Network. Hyperextended Knee-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatments
Jennifer Kirkman, Yahoo! Contributor Network. Hyperextended Knee-Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatments
5. what is genu recurvatum? http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-genu-recurvatum.htm.
6. Allison Cooper et al. The Relationship of Lower Limb Muscle Strength and Knee Joint hyperextension during the Stance Phase of Gait in Hemiparetic Stroke Patients. Journal of Physiotherapy research international.2011;(17)1.
7. Lucarli P et al. Alteration of load response mechanism of knee joint during hemiparetic gait following stroke. Journal of clinics.2007;22:813-820.
8. Susan Richardson. Assessing knee hyperextension in patients after stroke: comparing clinical observation and Siliconcoach software. International Journal of Therapy and Rehabilitation, Vol. 19, Iss. 3, 07 Mar 2012, pp 163 - 168. http://www.ijtr.co.uk/cgi-bin/go.pl/library/article.cgi?uid=90240;article=IJTR_19_3_163_168.
9. Bleyenheuft et al. Treatment of genu recurvatum in hemiparetic adult patients: A systematic literature review. Journal annals of physical and rehabilitation medicine.2010;53(3):189-199.
10. Rehabilitation, Treatment and Orthotic Management of the Stroke Patient. http://www.healio.com/orthotics-prosthetics/orthotics/news/online/%7BBDC02BFE-6C76-42E6-8457-462C3F6EC0B7%7D/Rehabilitation-Treatment-and-Orthotic-Management-of-the-Stroke-Patient